In thermoplastic elastomers, the look and feel of thermoset elastomers are combined with the processability of thermoplastics. However, with the right injection molding or extrusion process, manufacturers can create flexible materials with important thermoplastic properties. This is a big advantage of TPE materials. This article will review 7 Uses of Thermoplastic Elastomers, review their benefits, and examine how they are processed.
The uses of thermoplastic elastomers vary by industry. It is important to choose a TPE material that is compatible with the application it will be used in. Some common uses of TPE are shown below:
- Automotive: Due to their flexibility, excellent abrasion resistance, chemical and electrical resistance, and UV stability, TPEs are used extensively in automotive applications.
- Construction: Extrusion seals are made from TPE because of their durability and flexibility.
- Industrial: For applications such as anti-vibration mounts and springs, TPE has excellent damping properties.
- Consumer Products: TPE’s durability, flexibility, ease of molding, and chemical resistance are ideal for remote control housings and phone cases.
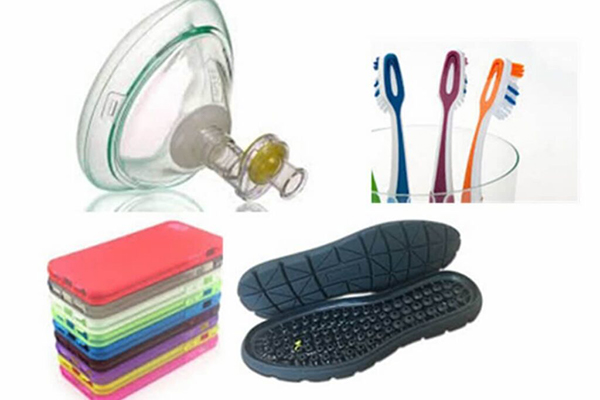
- Medical: TPE is flexible, biocompatible, lightweight, and chemically elastic. This makes it useful for breathing tubes, syringe seals, face masks, and other airtight seals.
- Electronics: TPEs are used in cell phone components, cables, plugs, and sockets due to their electrical resistance and molding capabilities.
- Sporting Goods: TPE is used in shoe soles, diving fins and ski pole handles for its flexibility, abrasion resistance, and UV stability.
1. Thermoplastic elastomers are used in automotive parts
Many automotive parts are made from thermoplastic elastomers. They find their way into areas such as seating and interior trim, weather seals, and floor mats. TPEs are ideal for automotive applications due to their excellent abrasion, chemical, and electrical resistance properties. Additionally, environmental resilience and UV stability make TPE ideal for automotive use as it will not degrade in direct sunlight.
2. Thermoplastic elastomers are used in construction materials
In construction, TPEs are used in the form of extruded seals for windows and doors, as well as other seals such as glass and pipe seals. TPEs are well suited for these applications because of their chemical and environmental resilience as well as their durability and flexibility.
3. Thermoplastic Elastomers for Industrial Applications
TPEs are used in industrial applications, especially to form seals and reduce vibrations. Uses include vibration isolators, springs and shock absorbers, roller suspension bushings as well as seals and o-rings. Due to their excellent damping capabilities, TPEs are well-suited for these applications.
4. Thermoplastic elastomers are used in consumer products
In consumer products, TPEs are often co-injected or over-molded onto a substrate with a separate plastic material. They are found in power tool handles, remote controls, cell phone cases, magnetic seals in refrigerators, and shock-absorbing components in vacuum cleaners. Due to their durability, flexibility, ease of molding, and chemical resistance, TPEs are used in a variety of consumer products.
5. Thermoplastic elastomers are used in medical supplies
TPE is commonly found in supplies such as breathing tubes, syringe tips, catheters, and masks. These materials are widely used in medical settings due to their excellent chemical resistance, biocompatibility, flexibility, and lightweight.
6. Thermoplastic elastomers are used in electronic equipment
TPE materials are often found in capacitors, plug and socket housings, cables, and smartphone components. They are ideal for such applications because they are non-conductive and easy to form.
7. Thermoplastic elastomers are used in footwear and sporting goods
TPE is used in shoe soles and a variety of sporting goods including ski equipment (shafts, boots) and diving equipment (fins, masks, and snorkels). TPE’s low density, flexibility, and abrasion resistance make it an excellent choice for footwear and sporting goods.
8. When is TPE used?
In applications requiring flexibility, TPEs are used. Many thermoplastics are much stiffer than TPEs and simply do not qualify for soft or flexible parts. This is where TPEs shine. In addition, TPEs are used in applications where chemical resistance, environmental resistance, and abrasion resistance are important.

9. Where can TPE be used as an alternative?
TPE can replace materials such as silicone, latex, and PVC compounds. For example, TPE can be used instead of latex to make TPE pillows. In contrast, TPEs are cheaper to manufacture but have similar properties – especially flexibility and hardness grades. Silicone, latex, and PVC compounds are difficult to convert into products. These materials often require additives as well as additional time for the material to cure in the mold. In addition, since TPE can be formed by automated processes such as injection molding or extrusion, it is easier to mass produce.
10. What are the most common production methods for TPE?
Injection molding and extrusion are the most common methods of processing TPE. However, blow molding, thermoforming, and 3D printing are also viable options. Unlike silicone, latex, and PVC compounds, TPEs do not require additional stabilizing agents, reinforcements, or curing systems. Therefore, TPEs are well-suited for high-volume injection molding or extrusion runs.
11. How are thermoplastic elastomers processed before use?
Unlike silicone, latex, and PVC compounds, TPE processing does not require additives to help it cure and cure. However, some TPE materials must be fully dried before processing. Drying the TPE ensures that excess moisture does not hinder manufacturing or affect the properties of the final material. Refer to the material data sheet for each resin to determine drying temperature and time.
12. What are the advantages of using thermoplastic elastomers?
Perhaps the biggest advantage of TPE is that it has the properties of a thermoset rubber, but can be formed using the same process as a thermoplastic. TPE’s light weight and excellent material properties make it ideal for certain applications. It is also less expensive to process than the materials it typically replaces, such as silicone, latex, and PVC compounds. TPEs are easy to color or dye, making them attractive for customer-facing parts.
13. What are the disadvantages of using thermoplastic elastomers?
Shear sensitivity, low odor resistance, and cost are some of the disadvantages of thermoplastic elastomers. TPE can be more expensive than thermoset rubber. Additionally, their low melting temperature makes TPE materials unsuitable for high-temperature applications.
14. Do thermoplastic elastomers use less energy to manufacture?
Compared to other thermoplastics, TPE uses less energy during processing. They attribute this advantage to the shorter cycle times of the injection molding machine or extruder.

15. Are thermoplastic elastomers a substitute for rubber?
TPE is used as a rubber substitute and is preferred in many cases. This is due to lower tooling costs, consistency of production, and desirable material properties.
16. Conclusion
This article discusses 7 uses of thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), along with the material’s advantages and limitations.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.








